The development of VLMs in the biomedical field faces challenges due to the lack of large-scale, annotated, publicly accessible multimodal datasets across various disciplines. Datasets are built from biomedical literature such as PubMed, but are often narrowly focused on areas such as radiology and pathology, with molecular biology and pharmacogenomics important to overall clinical understanding. Complementary areas such as are ignored. Privacy concerns, the complexity of expert-level annotation, and logistical constraints further impede the creation of comprehensive datasets. Previous approaches such as ROCO, MEDICAT, and PMC-15M relied on domain-specific filtering and supervised models to extract millions of image-caption pairs. However, these strategies often fail to capture the broader diversity of biomedical knowledge needed to advance generalist biomedical VLM.
In addition to dataset limitations, training and evaluation of biomedical VLMs presents unique challenges. Contrastive learning approaches such as PMC-CLIP and BiomedCLIP have shown promise by leveraging literature-based datasets and vision transformer models for image-text alignment. However, compared to typical VLMs, the smaller dataset and limited computational resources limit the performance. Furthermore, current assessment protocols primarily focus on radiology and pathology tasks and lack standardization and broad applicability. Reliance on additional learnable parameters or narrow datasets undermines the reliability of these evaluations, raising the need for scalable datasets and robust evaluation frameworks that can address the diverse demands of biomedical visual language applications. is highlighted.
Researchers at Stanford University introduced BIOMEDICA, an open-source framework designed to extract, annotate, and organize entire PubMed Central Open Access subsets into easy-to-use datasets. The archive contains more than 24 million image-text pairs from 6 million articles enriched with metadata and expert annotations. We also released BMCA-CLIP, a suite of CLIP-style models pre-trained on BIOMEDICA via streaming. This eliminates the need for local storage of 27 TB of data. These models deliver state-of-the-art performance across 40 tasks including radiology, dermatology, and molecular biology, with an average improvement of 6.56% in zero-shot classification and reduced computational requirements.
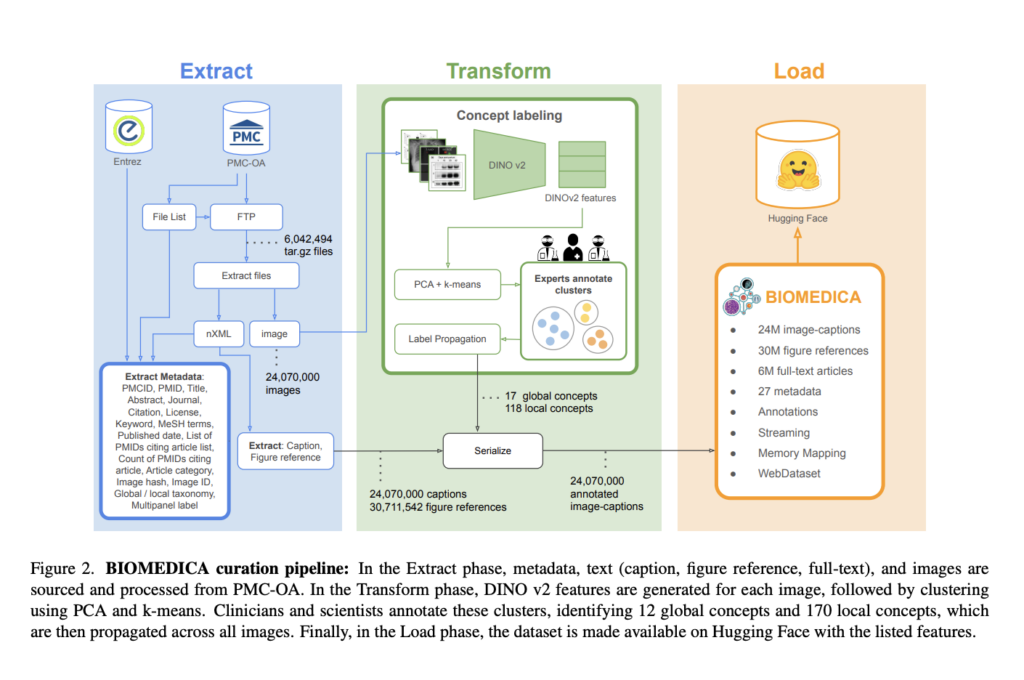
The BIOMEDICA data curation process includes dataset extraction, concept labeling, and serialization. Articles and media files are downloaded from NCBI servers, and metadata, captions, and figure references are extracted from nXML files and the Entrez API. Images are clustered using DINOv2 embeddings and labeled by a hierarchical classification refined by experts. Labels are assigned by majority vote and propagated throughout the cluster. This dataset contains over 24 million image-caption pairs and extensive metadata, serialized to WebDataset format for efficient streaming. With 12 global and 170 local image concepts, the taxonomy covers categories such as clinical imaging, microscopy, and data visualization, with an emphasis on scalability and accessibility.
The evaluation of continuous pre-training on the BIOMEDICA dataset leveraged 39 established biomedical classification tasks and a new search dataset from Flickr across 40 datasets. Classification benchmarks include tasks from pathology, radiology, biology, surgery, dermatology, and ophthalmology. Metrics such as average precision of classification and retrieval recall (1, 10, and 100) were used. Concept filtering, which excludes over-represented topics, performed better than concept balancing and pre-training on the complete dataset. The BIOMEDICA-trained model achieved state-of-the-art results that significantly outperformed previous methods, with improved performance across classification, search, and microscopy tasks with less data and computational effort.
In conclusion, BIOMEDICA is a comprehensive tool that transforms the PubMed Central Open Access (PMC-OA) subset into the largest deep learning-enabled dataset featuring 24 million image-caption pairs enriched with 27 metadata fields. It is a framework. BIOMEDICA is designed to address the lack of diverse annotated biomedical datasets, providing a scalable open-source solution for extracting and annotating multimodal data from over 6 million papers. Masu. Through continuous pre-training of CLIP-style models using BIOMEDICA, the framework delivers state-of-the-art zero-shot classification and image text retrieval across 40 biomedical tasks, requiring 10x less compute. The amount of data will be 2.5 times smaller. All resources, including models, datasets, and code, are publicly available.
Check out our papers and projects page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram channel and LinkedIn group. Don’t forget to join the 65,000+ ML SubReddit.
🚨 Recommended open source platform: Parlant is a framework that transforms the way AI agents make decisions in customer-facing scenarios. (promotion)
Sana Hassan, a consulting intern at Marktechpost and a dual degree student at IIT Madras, is passionate about applying technology and AI to address real-world challenges. With a keen interest in solving practical problems, he brings a new perspective to the intersection of AI and real-world solutions.
📄 Introducing Height: The Only Autonomous Project Management Tool (Sponsored)